*책 내용과 다르게, 다음과 같은 환경에서 프로젝트 생성
- Windows11(윈도우 11) 환경
- 자바 JDK 17 버전 설치 https://yungenie.tistory.com/11
[Java] 차근차근 Java 설치하기 (JDK17, Window 11)
자바 개발 도구 설치 방법에 대해서 알아보겠습니다. Java17은 LTS(Long Term Support : 장기 지원) 릴리즈로 1년 후까지 기술 지원 및 버그를 개선한 서비스를 제공받을 수 있습니다. 업데이트 버전을 꾸
yungenie.tistory.com
- 스프링 부트 4.31.0 사용 - STS(Spring Tool Suite) 설치(Spring Tools for Eclipse - https://spring.io/tools)
=> https://priming.tistory.com/147 참고
[Windows] Spring Tool Suite 4(STS 4) 다운로드 및 설치
STS란?Spring Tool Suite(STS)는 스프링 프로젝트를 생성하고, 개발할 수 있게 해주는 도구입니다. STS 설치 과정에 대해 설명드리겠습니다. 설치 파일 다운로드STS 공식 사이트에서 설치 파일을 다운로
priming.tistory.com

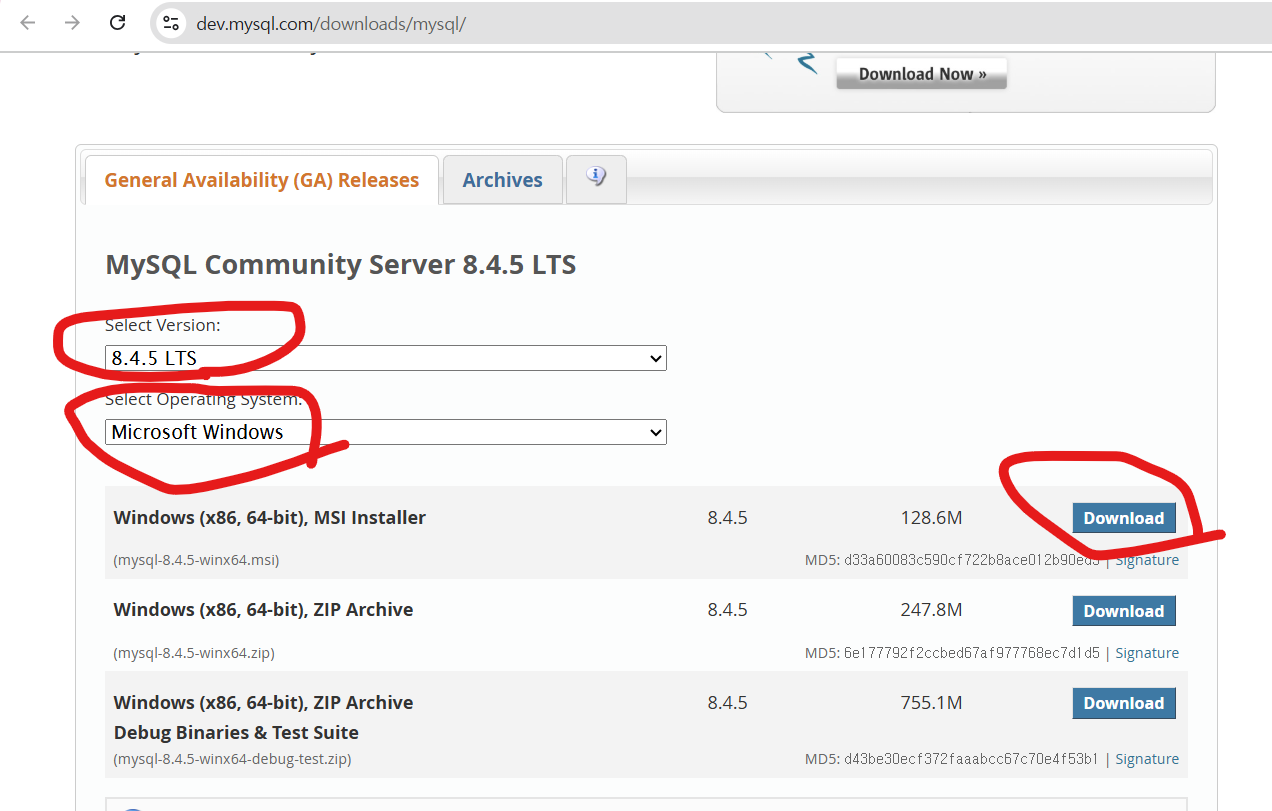
- MySQL Community Server 8.0.42 설치 https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/
MySQL :: Download MySQL Community Server
Select Version: 9.3.0 Innovation 8.4.5 LTS 8.0.42 Select Operating System: Select Operating System… Microsoft Windows Ubuntu Linux Debian Linux SUSE Linux Enterprise Server Red Hat Enterprise Linux / Oracle Linux Fedora Linux - Generic Oracle Solaris mac
dev.mysql.com
- Gradle
**STS에서 Gradle 프로젝트 생성한 과정

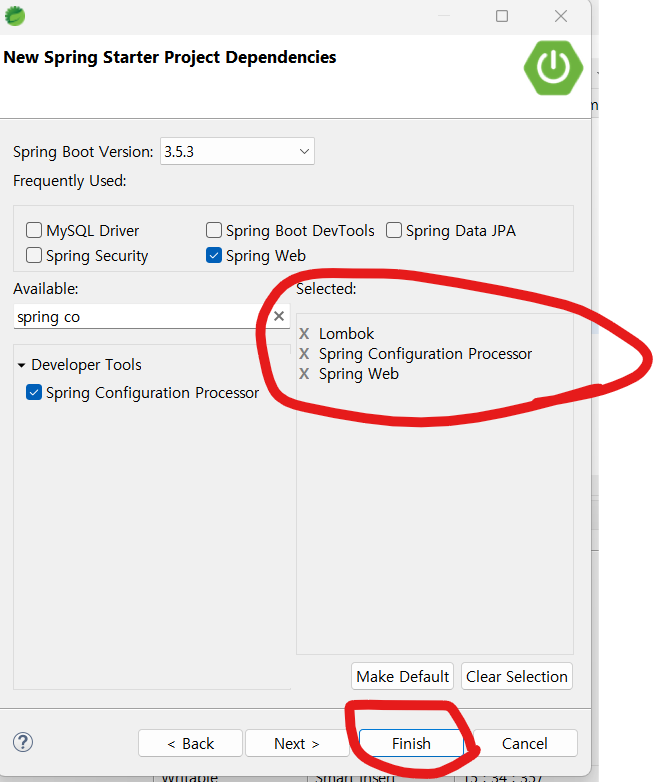
*** 함께 보면 좋은 글
스프링 부트 핵심 가이드(장정우 지음) - 스프링 부트 개요
1. 스프링 프레임워크자바(Java) 기반 애플리케이션 프레임워크로, 엔터프라이즈급(기업 환경 대상 개발) 애플리케이션을 위한 다양한 기능 제공-> 오픈소스 경량급 애플리케이션 프레임워크로
keep-programming-study.tistory.com
스프링 부트 핵심 가이드(장정우 지음) - 개발에 앞서 알면 좋은 기초 지식
1. 서버 간 통신마이크로서비스 아키텍처에서 한 서버가 다른 서버에 통신을 요청하는 것을 의미-> 한 대는 서버/다른 한 대는 클라이언트가 됨 가장 많이 사용되는 방식은 HTTP/HTTPS 방식(TCP/IP, SOA
keep-programming-study.tistory.com
2024.03.26 - [컴퓨터공학 공부/SQLD (SQL 전문가 가이드)] - SQLD 자격증 공부 데이터 모델링의 이해-엔터티, 속성(SQL 전문가가이드)
SQLD 자격증 공부 데이터 모델링의 이해-엔터티, 속성(SQL 전문가가이드)
*본 게시물은 2013년도 SQL 전문가 가이드 교재(일명 '노랭이')를 참고하여 공부하고 정리한 게시물입니다 1과목 데이터 모델링의 이해: 제1장 데이터 모델링의 이해 1. 엔터티 1) 정의 업무에서 관
keep-programming-study.tistory.com
JAVA/JSP 14. 데이터베이스 - 특징, 오라클 설치(Oracle Database 11gR2 Express Edition), 사용자 계정 생성 및
1. 데이터베이스의 특징우리가 매일 PC나 스마트폰을 통해 접하는 거의 모든 웹 애플리케이션에서 사용함매일 업데이트되는 뉴스나 날씨 등의 정보는 데이터베이스가 없다면 클라이언트에 전달
keep-programming-study.tistory.com
스프링 부트 핵심 가이드(장정우 지음) - 데이터베이스 연동 1: ORM(Object Relational Mapping) 특징, JPA(Ja
*책 내용과 다르게, 다음과 같은 환경에서 프로젝트 생성 Windows11(윈도우 11) 환경자바 JDK 17 버전 설치 https://yungenie.tistory.com/11 [Java] 차근차근 Java 설치하기 (JDK17, Window 11)자바 개발 도구 설치 방법
keep-programming-study.tistory.com
1. 프로젝트에 MySQL Community Server 연동
1) build.gradle에 의존성 추가
dependencies {
... 생략 ...
// Spring Boot에서 JPA(Java Persistence API) 기능을 사용하기 위한 의존성 추가
// -> Spring Data JPA 기능을 통해 리포지토리 인터페이스를 정의하기만 해도 자동으로 CRUD 메서드를 생성해줌
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
// MySQL 데이터베이스와 애플리케이션을 연결해주는 JDBC 드라이버 의존성을 추가(이 커넥터가 있어야만 DB와 통신할 수 있음)
// -> 'runtimeOnly'는 애플리케이션 실행 시에만 필요한 라이브러리라는 뜻이며, DB에 연결할 때 반드시 있어야 하는 요소
runtimeOnly 'com.mysql:mysql-connector-j'
}2) build.gradle 우클릭 후 Gradle -> Refresh Gradle Project 클릭

3) application.properties에 코드 추가 - 코드에 잘못된 부분이 있어 수정함(07/23)

# 데이터베이스 연결 정보 설정
# MySQL 서버에 연결할 주소, 포트, DB 이름을 지정. useSSL은 SSL 사용 여부, serverTimezone은 시간대 설정
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Seoul
# DB 접속 시 사용할 사용자 이름
spring.datasource.username=root
# DB 접속 시 사용할 비밀번호
spring.datasource.password=root
# 애플리케이션 실행 시 테이블 자동 생성/수정 여부 설정(운영 환경에서는 validate나 none을 사용)
# - create: 매번 새로 생성
# - update: 기존 테이블과 비교 후 수정
# - none: 아무 작업도 하지 않음
# - validate: 엔티티와 테이블 구조 일치 여부만 검증
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
# 실행되는 SQL 쿼리를 콘솔에 출력 (디버깅이나 학습에 유용)
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.application.name=study
# 데이터베이스 연결 정보 설정
# MySQL 서버에 연결할 주소, 포트, DB 이름을 지정. useSSL은 SSL 사용 여부, serverTimezone은 시간대 설정
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Seoul
# DB 접속 시 사용할 사용자 이름
spring.datasource.username=root
# DB 접속 시 사용할 비밀번호
spring.datasource.password=root
# 애플리케이션 실행 시 테이블 자동 생성/수정 여부 설정(운영 환경에서는 validate나 none을 사용)
# - create: 매번 새로 생성
# - update: 기존 테이블과 비교 후 수정
# - none: 아무 작업도 하지 않음
# - validate: 엔티티와 테이블 구조 일치 여부만 검증
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
# 실행되는 SQL 쿼리를 콘솔에 출력 (디버깅이나 학습에 유용)
spring.jpa.show-sql=true4) MySQL Workbench 설치 후 DB 생성
(1) MySQL Workbench 설치
- https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/workbench/ 에서 운영 체제를 Windows로 설정한 후 download를 클릭하여 설치


(2) MySQL Workbench에서 DB 생성


2. 엔티티 설계 & 리포지토리 인터페이스 설계
1) 엔티티 설계(엔티티 클래스 생성) - 코드에 잘못된 부분이 있어 수정함(07/23)
- @Column에서 많이 사용하는 다른 요소로는 name(칼럼명 설정), length(데이터 최대길이 설정), unique(중복 금지)가 있음
- 데이터베이스에서 엔티티를 이용하지 않을 경우, @Transient를 사용
// Product.java
package com.example.demo.jpa.data.entity;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import jakarta.persistence.Table;
//이 클래스는 JPA 엔티티로 데이터베이스 테이블과 매핑
@Entity
//엔티티가 매핑될 테이블 이름을 명시적으로 지정 (기본값은 클래스 이름)
@Table(name="product")
public class Product {
// 기본 키(PK)로 지정된 필드. 데이터베이스의 고유 식별자 역할
@Id
// ID 값을 자동 생성함. GenerationType.IDENTITY는 DB가 직접 AUTO_INCREMENT 방식으로 생성하도록 함(insert 후에 pk 자동생성)
// -> IDENTITY외에도 AUTO(기본값, 사용하는 데이터베이스에 맞게 기본값 자동 생성),
// SEQUENCE(Oracle, PostgreSQL 등 시퀀스를 지원하는 DB에서 별도 시퀀스 객체를 생성해 PK값 증가),
// TABLE(키 값을 관리하는 별도 테이블을 생성해 PK값 증가-성능 낮음)
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long number;
// 엔티티 클래스의 필드는 자동으로 테이블 칼럼으로 매핑되므로, 별다른 설정을 하지 않을 경우 @Column을 생략해도 됨
// 상품 이름 (Null 허용하지 않음)
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
// 가격 (Null 허용하지 않음)
@Column(nullable = false)
private int price;
// 재고 수량 (Null 허용하지 않음)
@Column(nullable = false)
private int stock;
// 상품 생성 일시 (자동 설정할 수 있으나 현재는 수동 할당 전제)
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
// 상품 수정 일시
private LocalDateTime updatedAt;
// Getter/Setter 메서드는 객체 지향의 캡슐화 원칙을 따름
// -> 필드에 직접 접근하지 않고 메서드를 통해 값 조회/수정하도록 하여 유연성과 안정성을 높임
public long getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(long number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getStock() {
return stock;
}
public void setStock(int stock) {
this.stock = stock;
}
public LocalDateTime getCreatedAt() {
return createdAt;
}
public void setCreatedAt(LocalDateTime createdAt) {
this.createdAt = createdAt;
}
public LocalDateTime getUpdatedAt() {
return updatedAt;
}
public void setUpdatedAt(LocalDateTime updatedAt) {
this.updatedAt = updatedAt;
}
}* Getter/Setter 메서드 자동생성 방법


2) 리포지토리 인터페이스 설계
- Spring Data JPA가 제공하는 JpaRepository 인터페이스를 기반으로 더욱 쉽게 사용할 수 있는 아키텍처 제공
-> JpaRepository를 상속하는 인터페이스를 생성하여 기존의 다양한 메서드를 활용 - 엔티티가 생성한 테이블에 접근하는 데 사용
(1) 리포지토리 인터페이스 생성
- 접근하려는 테이블과 매핑되는 엔티티에 대한 인터페이스를 생성하고, JpaRepository를 상속받으면 됨
package com.example.demo.jpa.data.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.example.demo.jpa.data.entity.Product;
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, Long> {
// Product 엔티티에 대한 CRUD + customMethod 사용 가능
}- 이때 위 코드에서 ctrl을 누르고 JpaRepository를 클릭하면 제공하는 기본 메서드 정보를 확인할 수 있음
/*
* Copyright 2008-2025 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.data.jpa.repository;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManager;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Example;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
import org.springframework.data.repository.ListCrudRepository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.ListPagingAndSortingRepository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.NoRepositoryBean;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.QueryByExampleExecutor;
/**
* JPA specific extension of {@link org.springframework.data.repository.Repository}.
*
* @author Oliver Gierke
* @author Christoph Strobl
* @author Mark Paluch
* @author Sander Krabbenborg
* @author Jesse Wouters
* @author Greg Turnquist
* @author Jens Schauder
*/
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface JpaRepository<T, ID>
extends ListCrudRepository<T, ID>, ListPagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID>, QueryByExampleExecutor<T> {
/**
* Flushes all pending changes to the database.
*/
void flush();
/**
* Saves an entity and flushes changes instantly.
*
* @param entity entity to be saved. Must not be {@literal null}.
* @return the saved entity
*/
<S extends T> S saveAndFlush(S entity);
/**
* Saves all entities and flushes changes instantly.
*
* @param entities entities to be saved. Must not be {@literal null}.
* @return the saved entities
* @since 2.5
*/
<S extends T> List<S> saveAllAndFlush(Iterable<S> entities);
/**
* Deletes the given entities in a batch which means it will create a single query. This kind of operation leaves JPAs
* first level cache and the database out of sync. Consider flushing the {@link EntityManager} before calling this
* method.
* <p>
* It will also NOT honor cascade semantics of JPA, nor will it emit JPA lifecycle events.
*
* @param entities entities to be deleted. Must not be {@literal null}.
* @deprecated Use {@link #deleteAllInBatch(Iterable)} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
default void deleteInBatch(Iterable<T> entities) {
deleteAllInBatch(entities);
}
/**
* Deletes the given entities in a batch which means it will create a single query. This kind of operation leaves JPAs
* first level cache and the database out of sync. Consider flushing the {@link EntityManager} before calling this
* method.
* <p>
* It will also NOT honor cascade semantics of JPA, nor will it emit JPA lifecycle events.
*
* @param entities entities to be deleted. Must not be {@literal null}.
* @since 2.5
*/
void deleteAllInBatch(Iterable<T> entities);
/**
* Deletes the entities identified by the given ids using a single query. This kind of operation leaves JPAs first
* level cache and the database out of sync. Consider flushing the {@link EntityManager} before calling this method.
*
* @param ids the ids of the entities to be deleted. Must not be {@literal null}.
* @since 2.5
*/
void deleteAllByIdInBatch(Iterable<ID> ids);
/**
* Deletes all entities in a batch call.
*/
void deleteAllInBatch();
/**
* Returns a reference to the entity with the given identifier. Depending on how the JPA persistence provider is
* implemented this is very likely to always return an instance and throw an
* {@link jakarta.persistence.EntityNotFoundException} on first access. Some of them will reject invalid identifiers
* immediately.
*
* @param id must not be {@literal null}.
* @return a reference to the entity with the given identifier.
* @see EntityManager#getReference(Class, Object) for details on when an exception is thrown.
* @deprecated use {@link JpaRepository#getReferenceById(ID)} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
T getOne(ID id);
/**
* Returns a reference to the entity with the given identifier. Depending on how the JPA persistence provider is
* implemented this is very likely to always return an instance and throw an
* {@link jakarta.persistence.EntityNotFoundException} on first access. Some of them will reject invalid identifiers
* immediately.
*
* @param id must not be {@literal null}.
* @return a reference to the entity with the given identifier.
* @see EntityManager#getReference(Class, Object) for details on when an exception is thrown.
* @deprecated use {@link JpaRepository#getReferenceById(ID)} instead.
* @since 2.5
*/
@Deprecated
T getById(ID id);
/**
* Returns a reference to the entity with the given identifier. Depending on how the JPA persistence provider is
* implemented this is very likely to always return an instance and throw an
* {@link jakarta.persistence.EntityNotFoundException} on first access. Some of them will reject invalid identifiers
* immediately.
*
* @param id must not be {@literal null}.
* @return a reference to the entity with the given identifier.
* @see EntityManager#getReference(Class, Object) for details on when an exception is thrown.
* @since 2.7
*/
T getReferenceById(ID id);
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
* @see org.springframework.data.repository.query.QueryByExampleExecutor#findAll(org.springframework.data.domain.Example)
*/
@Override
<S extends T> List<S> findAll(Example<S> example);
@Override
<S extends T> List<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Sort sort);
}- JpaRepository의 상속 구조

(2) 리포지토리 메서드의 생성 규칙
| findBy, readBy, getBy | 조회 시작 키워드 |
| And, Or | 조건 연결 |
| Is, Equals | 정확히 일치 |
| Between | 범위 조건 |
| LessThan, GreaterThan | 비교 조건 |
| Like, Containing, StartsWith, EndsWith | 문자열 검색 |
| In, NotIn | 리스트 포함 여부 |
| IsNull, IsNotNull | null 여부 |
| OrderBy + 필드명 + Asc/Desc | 정렬 |